To remove a directory:
# rmdir <name of directory>
The above command does not delete directories with contents in it. Use this command to delete directories with contents:
# rm -rf <name of directory>
To check the difference between 2 text files in Linux:
# diff <name of file 1> <name of file 2> eg: diff file1.txt file2.txt
To see the format of the file
# file <name of the file>
To find a file in a directory tree
# find dir -name <name of the file> -print
Shell input and output commands wbere i want to send an output to file instead of displaying onto the terminal. I use the redirection '>' character:
# <enter the command first, then the redirection> > test.txt
eg: df -l > check_disk.txt
To append the output to a file, simply issue the command again as shown above with another redirection char.
eg: df -l >> check_disk.txt
Thursday, 24 March 2011
Wednesday, 23 March 2011
Processes in Linux
To take a peek of process or to stop them is the same as what we do in windows where we right click on the task bar, click to open up the task manager.
The window will display all the processes currently running in windows. To stop or kill the processes, simply select one of them and click on the 'End Task' button.
So how do i do in Unix? When i display the processes in unix, the terminal will display these information on the window:
PID = process id
TTY = terminal device where process is running
STAT = Process stats
TIME = Amount of CPU time used
COMMAND = Command of the process
To view the detailed report of the process:
# ps ax or # ps u or # ps -ef
To kill a process, simply issue the above command, look for the PID number and issue this command with the number:
# kill <ENTER THE PID_NUMBER>
To freeze or stop a process
# kill -STOP <ENTER THE PID_NUMBER>
To restart a process again
# kill -CONT <ENTER THE PID_NUMBER>
The window will display all the processes currently running in windows. To stop or kill the processes, simply select one of them and click on the 'End Task' button.
So how do i do in Unix? When i display the processes in unix, the terminal will display these information on the window:
PID = process id
TTY = terminal device where process is running
STAT = Process stats
TIME = Amount of CPU time used
COMMAND = Command of the process
To view the detailed report of the process:
# ps ax or # ps u or # ps -ef
To kill a process, simply issue the above command, look for the PID number and issue this command with the number:
# kill <ENTER THE PID_NUMBER>
To freeze or stop a process
# kill -STOP <ENTER THE PID_NUMBER>
To restart a process again
# kill -CONT <ENTER THE PID_NUMBER>
Tuesday, 22 March 2011
Groups in Linux
Sometimes i need to add myself into other groups to access certain files or accessing a software.
Currently this is what i have set up for my linux machine. I prefer to have only 1 initial group. In my opinion, the best way is to have users as the initial group. (This varies for different players or grouping patterns in different environment)
To set myself in the initial group in users:
# usermod -g users chongming
To add myself into other groups:
#gpasswd -a chongming audio
#gpasswd -a chongming video
#gpasswd -a chongming floppy
#gpasswd -a chongming cdrom
#gpasswd -a chongming plugdev
Thats the end to groups in Slackware linux
Currently this is what i have set up for my linux machine. I prefer to have only 1 initial group. In my opinion, the best way is to have users as the initial group. (This varies for different players or grouping patterns in different environment)
To set myself in the initial group in users:
# usermod -g users chongming
To add myself into other groups:
#gpasswd -a chongming audio
#gpasswd -a chongming video
#gpasswd -a chongming floppy
#gpasswd -a chongming cdrom
#gpasswd -a chongming plugdev
Thats the end to groups in Slackware linux
Reading the Tsung Reports
This post is to explain the reading of the Tsung reports generate by the Tsung benchmarking tool as shown in my last post.
Below are the screen shots of the reports which Tsung has generate:
Next these are Tsung reports based in graphical description:
Lastly, these are the explanation of the reports which can give the testers some ideas or guidelines on what was going on during the testing.
Reading the report
Network Throughput
The size received and size sent are measured on the ethernet packets sent or received on each hosts during the test.
The size received and size sent are measured on the ethernet packets sent or received on each hosts during the test.
Counters Statistics
The highest rate is the computation of the average of rate every 10 secs. The highest rate is the maximum value for all these estimations.
The Max value for the counter statistics are refering to the number of simultaneous connected users and simultaneous alive users.
The users_count is the number of users created and finished_user_count is the total number of users who complete the test.
Http Response code
Status-Code =
"100" ; Section 10.1.1: Continue
| "101" ; Section 10.1.2: Switching Protocols
| "200" ; Section 10.2.1: OK
| "201" ; Section 10.2.2: Created
| "202" ; Section 10.2.3: Accepted
| "203" ; Section 10.2.4: Non-Authoritative Information
| "204" ; Section 10.2.5: No Content
| "205" ; Section 10.2.6: Reset Content
| "206" ; Section 10.2.7: Partial Content
| "300" ; Section 10.3.1: Multiple Choices
| "301" ; Section 10.3.2: Moved Permanently
| "302" ; Section 10.3.3: Found
| "303" ; Section 10.3.4: See Other
| "304" ; Section 10.3.5: Not Modified
| "305" ; Section 10.3.6: Use Proxy
| "307" ; Section 10.3.8: Temporary Redirect
| "400" ; Section 10.4.1: Bad Request
| "401" ; Section 10.4.2: Unauthorized
| "402" ; Section 10.4.3: Payment Required
| "403" ; Section 10.4.4: Forbidden
| "404" ; Section 10.4.5: Not Found
| "405" ; Section 10.4.6: Method Not Allowed
| "406" ; Section 10.4.7: Not Acceptable
| "407" ; Section 10.4.8: Proxy Authentication Required
| "408" ; Section 10.4.9: Request Time-out
| "409" ; Section 10.4.10: Conflict
| "410" ; Section 10.4.11: Gone
| "411" ; Section 10.4.12: Length Required
| "412" ; Section 10.4.13: Precondition Failed
| "413" ; Section 10.4.14: Request Entity Too Large
| "414" ; Section 10.4.15: Request-URI Too Large
| "415" ; Section 10.4.16: Unsupported Media Type
| "416" ; Section 10.4.17: Requested range not satisfiable
| "417" ; Section 10.4.18: Expectation Failed
| "500" ; Section 10.5.1: Internal Server Error
| "501" ; Section 10.5.2: Not Implemented
| "502" ; Section 10.5.3: Bad Gateway
| "503" ; Section 10.5.4: Service Unavailable
| "504" ; Section 10.5.5: Gateway Time-out
| "505" ; Section 10.5.6: HTTP Version not supported
| extension-code
Main Statistics
Connect is the duration of the connection establishment
Request is the response time for each requests
Page is Response time for each set of requests (a page is a group of request not separated by a thinktime)
Session is the duration of a user session
Error Connection
Error connection is calculate every 10 secs. Below is an example
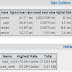
Name Highest Rate Total Number
Connect is the duration of the connection establishment
Request is the response time for each requests
Page is Response time for each set of requests (a page is a group of request not separated by a thinktime)
Session is the duration of a user session
Error Connection
Error connection is calculate every 10 secs. Below is an example
Name Highest Rate Total Number
Error connection timeout 2/sec 68
For every 10 sec, tsung will dump all its counters for calculation. Therefore the explanation for Highest rate is throughout the whole session,for 10 secs, maximum of timeout found is 2 per second.
Monday, 21 March 2011
Graham and Dodd, Security Analysis Chap 5: Survey and Approach
This is typically a short chapter discussing about the difference between bonds and stock by the gurus.
They have identified that many investors regard bonds as a safe investment which leds to investor to believe that bonds carry assurance against loss.This line is extracted from the book: Safety depends upon and is measured entirely by the ability of the debtor corporation to meet its obligations
They stated that bonds are not consider to be safe if it does not have these critera:
Good earning power of a company
A business with abundant of assets
A bond bought at a low price works like a common stock due to its coupon payments which act like dividends & the appreciation of bond price to par is the same as a common stock with its value appreciating
A bond bought with at high price, callable or convertible is not consider as safe investment as these may be some of the possibilities that an investor might face:
They have identified that many investors regard bonds as a safe investment which leds to investor to believe that bonds carry assurance against loss.This line is extracted from the book: Safety depends upon and is measured entirely by the ability of the debtor corporation to meet its obligations
They stated that bonds are not consider to be safe if it does not have these critera:
Good earning power of a company
A business with abundant of assets
A bond bought at a low price works like a common stock due to its coupon payments which act like dividends & the appreciation of bond price to par is the same as a common stock with its value appreciating
A bond bought with at high price, callable or convertible is not consider as safe investment as these may be some of the possibilities that an investor might face:
- investor may overpay for the bonds
- the calling of the bonds by the issuer can force the investor to look another investment & put a stop to his recurring income
- lastly, the investor faces reinvestment risk as when his bonds are called, he is force to invest his capital at a lower rate
IDX-Tsunami/Tsung: Benchmark Testing on the App Server
Today i sure list the steps and ways to use the Tsung tool to check how much stress/load the server could take.
I have use Geronimo to test out the effectiveness of tsung. Previously i have tested it out on Jboss to determine the performance of the application while i was working in my last company. The results are marvelous and we did what we could to improve the areas of the application before it goes live.
Below are the steps to use the tsung benchmarking tool.
Start the Geronimo Application Server in Unix
Open up the web browser and type in the url to access the application. eg: http://localhost:8080/TEST/start.jsp
Next enter this command to start up Tsung
# tsung start
To stop Tsung, enter the command below
# tsung stop
In the print screen below, you may have notice that tsung sends notification on the terminal indicating that the tsung recorder is not started. Do not worry about that as the recorder is to records users ways of using the system and Tsung will generate a scenario xml file to stress test the application.
to check the number of users being simulate during testing on the terminal
# tsung status
The figure below is a brief report on its status in testing the application
Next generate the reports for the Geronimo testing
cd into the tsung folder when the data is store
Now lets type the commands to generate the reports from the test
I will list down the reports next time once i have compile all the screenshots ready to be upload into the system.
Hope Tsung helps you to stress test your application.
Friday, 18 March 2011
Installing the WICD software to scan for wireless ip address
WICD is fd and wireless network manager for Linux.
Some features include:
- Ability to connect to wired and wireless networks
- Profiles for each wireless network and wired network
- Many encryption schemes, some of which include WEP/WPA/WPA2
- Compatible with wireless-tools
I'm installing this software in my linux machine. So after installing, i need to start up the Wicd in my machine by opening up a terminal:
# su root
# key in my root password
Start up Wicd by executing this command:
# wicd
However the method above requires me to start up the wicd everytime when i restart my machine. Therefore i chose to edit the rc.d file to start up wicd automatically.
Check your /etc/rc.d directory and make sure rc.wicd is executable
Using vi editor, add in these lines into the file
Some features include:
- Ability to connect to wired and wireless networks
- Profiles for each wireless network and wired network
- Many encryption schemes, some of which include WEP/WPA/WPA2
- Compatible with wireless-tools
I'm installing this software in my linux machine. So after installing, i need to start up the Wicd in my machine by opening up a terminal:
# su root
# key in my root password
Start up Wicd by executing this command:
# wicd
However the method above requires me to start up the wicd everytime when i restart my machine. Therefore i chose to edit the rc.d file to start up wicd automatically.
Check your /etc/rc.d directory and make sure rc.wicd is executable
Using vi editor, add in these lines into the file
if [ -x /etc/rc.d/rc.wicd ]; thenRestart my machine to check if it load wicd automatically
/etc/rc.d/rc.wicd start
fi
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
Cash flow Forecasting
Why cash forecasting? A cash forecasting model is an essential tool for treasuer to manage working capital. Forecasting preempt treasurer ...
-
What is POBO? POBO it's actually referring to Payments On Behalf Of. It is actually a method of centralizing payments initiation to ma...
-
This post is to explain the reading of the Tsung reports generate by the Tsung benchmarking tool as shown in my last post. Below are the scr...
-
I received a question asking me what is the difference between Treasury Centre (TC), In-house bank (IHB) and Shared Services Centre (SSC). ...