I will like to say Thanks to my previous company for recognizing my efforts and i greatly appreciated the honour you have given me.
Tuesday, 2 October 2012
Sunday, 17 July 2011
Configure a POP3 service on virtualised Linux machine.
1) Download the IMAP tarball from this website:
IMAP/POP Homepage: http://www.washington.edu/imap/
IMAP/POP Homepage: http://www.washington.edu/imap/
2) Unzip the file with the command
tar -zxvf imap.tar.Z
3) Move into the folder and edit the Makefile:
cd /home/chongming/Desktop/imap-2006e
vi Makefile
4) Change the SSLTYPE=none
Save and exit the file.
5) Make the file:
make lnp
And type y to continue building
6) Move into ipopd directory
cd /ipopd
cp ipop3d /usr/local/bin
7) Move into /etc/xinetd.d and create a file call pop3d into the directory
cd /etc/xinetd.d
vi pop3d
8) Create a PAM authentication to the service. Create imap and pop files into
/etc/pam.d
cd /etc/pam.d
vi pop
Vi imap
9) Start sending mail to chongming with sender as root
10) Using pop3 server to retrieve mail
11) Edit the muttrc file
12) Start to read mail using mutt
The message will appear upon selecting yes to view the message as shown below.
Tuesday, 19 April 2011
My requirements process: How i look at a process for gathering requirements
I have created a short requirement analysis based on a company doing e-commerce payments system. I have not talk to any of the stakeholders and the information i gathered is based on its software workflow and the information it provides on their webpage.
我用一个公司创建电子商务的支付系统创建了一个简短的需求分析. 我的资料收集是基于其软件的工作流程和我所收集的资料, 都是从他们的网页读和分析的。
When i need to gathered requirements, this is how i will look at a process before implementing the necessary codes to create a system.
当我需要收集需求分析资料的时候,这就是我会在这个过程看在实施必要,然后再创建一个系统。
A short example of my use-case:
For their system doing payments, i will list down the key payment business rules in the system.
This alternative case scenarios states how payers will get to choose their desired payments and system will wait for their input before processing.
In any case, sometimes we need to cater for systems that encounter exception scenarios for eg: Something disrupts the workflow and how we can introduce solutions to rectify them
Lastly some of the test cases that we can implemented to make sure the system is well prepared for users usage:
我用一个公司创建电子商务的支付系统创建了一个简短的需求分析. 我的资料收集是基于其软件的工作流程和我所收集的资料, 都是从他们的网页读和分析的。
When i need to gathered requirements, this is how i will look at a process before implementing the necessary codes to create a system.
当我需要收集需求分析资料的时候,这就是我会在这个过程看在实施必要,然后再创建一个系统。
A short example of my use-case:
For their system doing payments, i will list down the key payment business rules in the system.
Types of Payments from users with different sets of business rules:
- Credit Cards
- Debit Cards
- E-Giro
- Remittance
- Mobile E-banking users
- Pay-pal
- Corporate Accounts
- Bank branches/Foreign banks
Scenario breakdown:
- Get the user account number and location
- Send the credentials
- Check and verify
- Ask security questions
- Permit access to the account
- View payment items
- User confirms the payment and sends in the payment details
- Business rules to determine the type of settlement services
- Confirm the settlement at the back office
- Confirm settlement to user
Normal Case Scenarios
1. Inputs: User account, password, objects to make payments for. Output: Records inserted into the back end and confirmation made to the payer
The payer’s account number, password, purchased items and his account are both constraints on the work. His account number comes from outside, which is the account number & password that he needs to input. The record account is a constraint imposed by the bank system; in this case, it cannot be changed.
However, the account number, password, purchased items and his account are means to an end the real work to be done is to make the payment transaction.
2. The implementation of the security encapsulation protocols to transfer data
The use of the security features such as SSL to transfer payer details
3. Ensure the payer is correctly identified and connected to the right account.
4. Check the payer account is valid and belongs to the payer.
- The account must be current in used.
- Enough funds in his account
- Credit limit is not exceed
- Displays his payment history
What is the main goal of this process?
Business Event: Payer decides to make payment
What are the information that must be available before the system will starts the functions?
Trigger: Payers account, password, purchased items list/payment items, account database
Preconditions: The payer must have an account
Interested stakeholders: Types of payment account(Visa, Mastercard, E-banking, Paypal, etc), Payment List, workflow, security, goal of the transaction
Active stakeholders: Payer, Institutions
- Verify the payer’s account
- Transfer data using security encryption
- Check the account is valid
- Check with business rules to ensure the account can be used.
- Verify the items which payment is to be made
- Select the type of payment
- Check with the business rules to select the type gateway
- Process with payment and record in the backend
- Process with payment and sends confirmation to payer.
This alternative case scenarios states how payers will get to choose their desired payments and system will wait for their input before processing.
Alternative Case Scenarios
5. Using payment Gateway to make payments
In this scenario, alternative case can arrive when it comes to choosing which payment gateway.
Consider this step 5 scenario:
- Choose to use the Visa/Master, Paypal, and etc gateway based on business rules engine to select payers’ payment preferences
- Using the guiding payment rules to facilitate the transaction work flow
Exception Cases
6. The goal of this exception case is to show how we can handle exceptions when the business workflow deviates from the goal.
Some of the exceptions can be:
- What happens if the server is loaded and transaction process is taking a long time?
- What happens if there is error encountered while inserting records in the database?
- What can go wrong in these steps?
Solutions:
- Some solutions to solve the stress of the servers can be using the load balancer to move the load of users to different servers
- Using the cluster server to handle the load, for eg: if one of the server is down, the second server can be kick start to continued the process
- Implement the functions in the business rules to synchronize the methods for inserting data
- Solutions to handle the error in data insertion will be having a rollback mechanism in the business logic to prevent duplications or dirty records
Misuse Cases & Negative Scenarios
7. This case may surface when an antagonist uses someone’s account to make transactions.
Scenarios to stop/prevent the misuse
- The payer key in an incorrect password for an account that is not his
- Allow the antagonist to key in 3 times (this is for ebanking account)
- Freeze/lock the account when the password is incorrect(this is for ebanking account)
- Send an sms if payment exceed a certain amount (for credit cards)
Outcome
The payment is make successfully, records retained at the institutions’ backend and confirmation make to payers’ records.
Lastly some of the test cases that we can implemented to make sure the system is well prepared for users usage:
Types of testing to deployed
- Unit Testing (Component Testing) – testing of individual module components as they are completed.
- Integration Testing – testing to integrate multiple modules
- User Acceptance Testing – testing by users/customer to get approval that business flow is correct and what they want
- Functional Testing (Black Box Testing) – testing done to ensure the final output is what the user/customers want
- Usability Testing – testing for users where they can get to understand more about the application, as well as the users’ efficiency and productivity.
- Performance Testing (Load Testing, Stress Testing) – refers to testing performed to evaluate whether the system. Eg: Use idx-tsunami stress tool to simulate a high number of users and emulate the using of the system at the same time
Chapter 27: Theory of Common stock investment
According to the the authors, stock analysis are commonly impaired by 2 factors:
Author classify investment stock as:
New era theory
The law of diminishing returns
Increased competitiveness from competitors
The ups and downs of the economy cycle where the company stock may look impressive due to the fact that it is at the top cycle of the economy cycle and as the law of nature states, what goes up will go down eventually. Therefore beware of buying at this time and the fall of the economy cycle will bring down the profits of the company
- The instability of the tangible assets as most of the time, they are not worth the exact market value when the company is distress or deflation in economy
- The difficulty of estimating the intangibles assets and most of the time, they do not worth as much as what the management sees. However there are some exceptions where a company worth depends on its intangibles such as Coca Cola.
- It paid no dividends
- Earnings where irregular and sometimes its profits may cover barely its expenses
- A stated part of its stated value represented no actual investment in business
Author classify investment stock as:
- Earnings where stabke abd in excess of dividends paid
- Having a satisfactory record of dividend handouts to investors
- each dollar of stock was backed by a dollar or more of actual investment in business
New era theory
- In this era, investors look for investments by looking at dividends and believe that it has a slight bearing upon the value
- No relationship existed between assets and earning power, asset value was entirely devoid of importance
- Pas earnings are use to estimate what changes were likely to take place in future and not using it to estimate the stability of a company
The law of diminishing returns
Increased competitiveness from competitors
The ups and downs of the economy cycle where the company stock may look impressive due to the fact that it is at the top cycle of the economy cycle and as the law of nature states, what goes up will go down eventually. Therefore beware of buying at this time and the fall of the economy cycle will bring down the profits of the company
Friday, 1 April 2011
Lets use Commands for Linux Partitioning
Nowadays with so much improvements contribute to Linux makes this OS easier for the users as compared 10 yrs ago.
1 significant improvement to Linux is the partition of the disk. Users in these days can simply use the GUI interface or software such as G-Part to partition instead of using commands.
However for me, being a fan of Linux OS, it will be somehow a feeling of dissatisfaction without trying to partition using Linux commands. Today i will blog how i partition using the hard disk in Linux without using GUI.
To save time and to print some screens on how it works, i will use DLX OS using the Bochs Virtual Environment. Below are the steps of how i install DLX into Bochs Env using the Windows system. If you happened to read this post and you like to try partitioning using Linux, simply skip the Bochs part:)
如今有这么多的改善作出贡献的Linux,更十多年前比起来,真的是比较容易多了。
一个显着改善Linux,就是磁盘分区。
在这个世纪里,用户可以简单地使用GUI界面或如G-Part软件进行分区,而不是使用Unix/Linux的命令。
然而,对于我来说,Linux操作系统的风扇喜爱者,不尝试使用Unix/Linux的命令分区磁盘,将是某种的不满情绪.
今天我将博客我是如何分区硬盘,不使用GUI界面在Linux。
为了节省时间,并打印它是如何工作的一些画面,我将用DLX的操作系统使用Bochs的虚拟环境。
下面是我的步骤,如何使用Windows系统安装 DLX在 Bochs的环境中。
如果你碰巧看到这篇文章,你想尝试使用Linux分区,请跳过Bochs这一部分
First i create a disk image in Bosch as shown below:
博世创建一个磁盘映像:
After setting the necessary partition, we need to write/register the partitions.
Enter or type 'w' to write the partition into the system. It should return: 'Partition table has been altered'
在设置了必要的分区,我们需要编写/注册分区。
Below is the confirmation of creating the file systems:
1 significant improvement to Linux is the partition of the disk. Users in these days can simply use the GUI interface or software such as G-Part to partition instead of using commands.
However for me, being a fan of Linux OS, it will be somehow a feeling of dissatisfaction without trying to partition using Linux commands. Today i will blog how i partition using the hard disk in Linux without using GUI.
To save time and to print some screens on how it works, i will use DLX OS using the Bochs Virtual Environment. Below are the steps of how i install DLX into Bochs Env using the Windows system. If you happened to read this post and you like to try partitioning using Linux, simply skip the Bochs part:)
如今有这么多的改善作出贡献的Linux,更十多年前比起来,真的是比较容易多了。
一个显着改善Linux,就是磁盘分区。
在这个世纪里,用户可以简单地使用GUI界面或如G-Part软件进行分区,而不是使用Unix/Linux的命令。
然而,对于我来说,Linux操作系统的风扇喜爱者,不尝试使用Unix/Linux的命令分区磁盘,将是某种的不满情绪.
今天我将博客我是如何分区硬盘,不使用GUI界面在Linux。
为了节省时间,并打印它是如何工作的一些画面,我将用DLX的操作系统使用Bochs的虚拟环境。
下面是我的步骤,如何使用Windows系统安装 DLX在 Bochs的环境中。
如果你碰巧看到这篇文章,你想尝试使用Linux分区,请跳过Bochs这一部分
First i create a disk image in Bosch as shown below:
博世创建一个磁盘映像:
Now i will copy the DLX image into the Bochs directory.
复制DLX形象到Bochs的目录中
The boch.bxrc file.
boch.bxrc文件。
Now go into the dxlinux and click on the run.bat file to start the program. I will be looking at the screen as shown below:
点击进入dxlinux和澳run.bat文件.
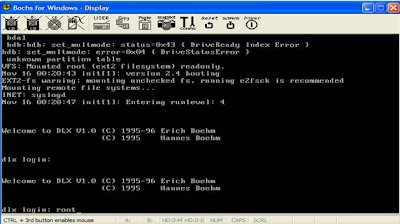
Log in as root:
以root身份登录:
Start partioning the drive.
开始磁盘分区
开始磁盘分区
Type fdisk –l to see the status of the disk:
Type fdisk /dev/hdb to start portioning
The steps below are used to partition in sequence.40M means 40MB
下面的步骤是用来磁盘分区
- Select ‘p’ to partition.
- Enter 1 to partion hdb1
- Enter 40M for memory
- Enter ‘n’ to partition
- Enter ‘p’
- Enter 2 to partition hdb2
- Enter 40M for memory
- Repeat the steps of 1 to 7, however at step 2, enter 3 and 4 to partition each HD respectively as well as hdb3 for 10M and hdb4 for 10M
- In total based on the steps just listed, i'm creating 4 partitions. Normally we create partitions for root partition, home partition and swap partition. I prefer to create another 1 more partition to store important documents or files.
- 在对刚刚上市的步骤的基础总额,我创建4个分区。
Enter or type 'w' to write the partition into the system. It should return: 'Partition table has been altered'
在设置了必要的分区,我们需要编写/注册分区。
Now check the partition of my disk using fdisk -l. It should list 4 partitions in the disk.
检查我的磁盘分区使用fdisk- 1
Lets create the file systems for each individual partitions by typing the following commands:
创建文件系统:
1) mke2fs /dev/hdb1
2) mke2fs /dev/hdb2
3) mke2fs /dev/hdb3
4) mke2fs /dev/hdb4
Below is the confirmation of creating the file systems:
Now i will be creating directories and mount each directory to a partition. Its like mounting a thumbdrive into Linux. To mount, we need to create a directory so that it can connect to the thumbdrive or partition and we can access the data in the partition by accessing the directory.
Create the 4 directories first (any name i want)
创建目录和每个目录挂载到分区。:
创建目录和每个目录挂载到分区。:
- mkdir /web
- mkdir /usr/local
- mkdir /usr/local/spare
- mkdir /home
Mounting the partitions to the respective directories.
- Mount –a /dev/hdb1 /home
- Mount –a /dev/hdb2 /usr/local
- Mount –a /dev/hdb3 /usr/local/spare
- Mount –a /dev/hdb4 /usr/home
Type df-k to see the mounted directories:
This should end how to partition and mounting of file systems.
这应该结束如何分区和文件系统的安装。
Thursday, 24 March 2011
Commands for files and directories in Unix /Linux Suse
To remove a directory:
# rmdir <name of directory>
The above command does not delete directories with contents in it. Use this command to delete directories with contents:
# rm -rf <name of directory>
To check the difference between 2 text files in Linux:
# diff <name of file 1> <name of file 2> eg: diff file1.txt file2.txt
To see the format of the file
# file <name of the file>
To find a file in a directory tree
# find dir -name <name of the file> -print
Shell input and output commands wbere i want to send an output to file instead of displaying onto the terminal. I use the redirection '>' character:
# <enter the command first, then the redirection> > test.txt
eg: df -l > check_disk.txt
To append the output to a file, simply issue the command again as shown above with another redirection char.
eg: df -l >> check_disk.txt
# rmdir <name of directory>
The above command does not delete directories with contents in it. Use this command to delete directories with contents:
# rm -rf <name of directory>
To check the difference between 2 text files in Linux:
# diff <name of file 1> <name of file 2> eg: diff file1.txt file2.txt
To see the format of the file
# file <name of the file>
To find a file in a directory tree
# find dir -name <name of the file> -print
Shell input and output commands wbere i want to send an output to file instead of displaying onto the terminal. I use the redirection '>' character:
# <enter the command first, then the redirection> > test.txt
eg: df -l > check_disk.txt
To append the output to a file, simply issue the command again as shown above with another redirection char.
eg: df -l >> check_disk.txt
Wednesday, 23 March 2011
Processes in Linux
To take a peek of process or to stop them is the same as what we do in windows where we right click on the task bar, click to open up the task manager.
The window will display all the processes currently running in windows. To stop or kill the processes, simply select one of them and click on the 'End Task' button.
So how do i do in Unix? When i display the processes in unix, the terminal will display these information on the window:
PID = process id
TTY = terminal device where process is running
STAT = Process stats
TIME = Amount of CPU time used
COMMAND = Command of the process
To view the detailed report of the process:
# ps ax or # ps u or # ps -ef
To kill a process, simply issue the above command, look for the PID number and issue this command with the number:
# kill <ENTER THE PID_NUMBER>
To freeze or stop a process
# kill -STOP <ENTER THE PID_NUMBER>
To restart a process again
# kill -CONT <ENTER THE PID_NUMBER>
The window will display all the processes currently running in windows. To stop or kill the processes, simply select one of them and click on the 'End Task' button.
So how do i do in Unix? When i display the processes in unix, the terminal will display these information on the window:
PID = process id
TTY = terminal device where process is running
STAT = Process stats
TIME = Amount of CPU time used
COMMAND = Command of the process
To view the detailed report of the process:
# ps ax or # ps u or # ps -ef
To kill a process, simply issue the above command, look for the PID number and issue this command with the number:
# kill <ENTER THE PID_NUMBER>
To freeze or stop a process
# kill -STOP <ENTER THE PID_NUMBER>
To restart a process again
# kill -CONT <ENTER THE PID_NUMBER>
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
Cash flow Forecasting
Why cash forecasting? A cash forecasting model is an essential tool for treasuer to manage working capital. Forecasting preempt treasurer ...
-
What is POBO? POBO it's actually referring to Payments On Behalf Of. It is actually a method of centralizing payments initiation to ma...
-
This post is to explain the reading of the Tsung reports generate by the Tsung benchmarking tool as shown in my last post. Below are the scr...
-
I received a question asking me what is the difference between Treasury Centre (TC), In-house bank (IHB) and Shared Services Centre (SSC). ...